March 2017, v.1.2
Updated: September 2017
Feedback/Comments :: View Release Notes
- Overview
- Methodology
- Background
- Biochemical Pathway and Nutrition Treatment Rationale
- Nutrition Assessment
- Comparative Standards
- Nutrition Problem Identification
- Nutrition Intervention
- Nutrition Recommendations
- Monitoring and Evaluation
- Resources
- Benefits and Harms of Implementing the Recommendations
- Barriers to Implementation
- Areas for Future Research
- List of Tables
-
Literature Evidence Summary Tables
- T.1 Clinical Symptoms and Laboratory Findings in PROP
- T.2 Nutrition Problem Identification for PROP based on the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Nutrition Care Process
- T.3 Recommended Intakes of PRO and Energy for Well Individuals with PROP
- T.4 Classification of Medical Foods for the Nutrition Management of PROP
- T.5 Nutrient Sources in the Nutrition Management of Well Individuals with PROP
- T.6 Nutrition Management of Individuals with PROP
- T.7 Monitoring the Nutritional Management of Well/Stable Individuals with PROP
- References
- Contributors
- Appendix A: Recommendation Rating Definitions
- Appendix B: Terms
- Disclaimer
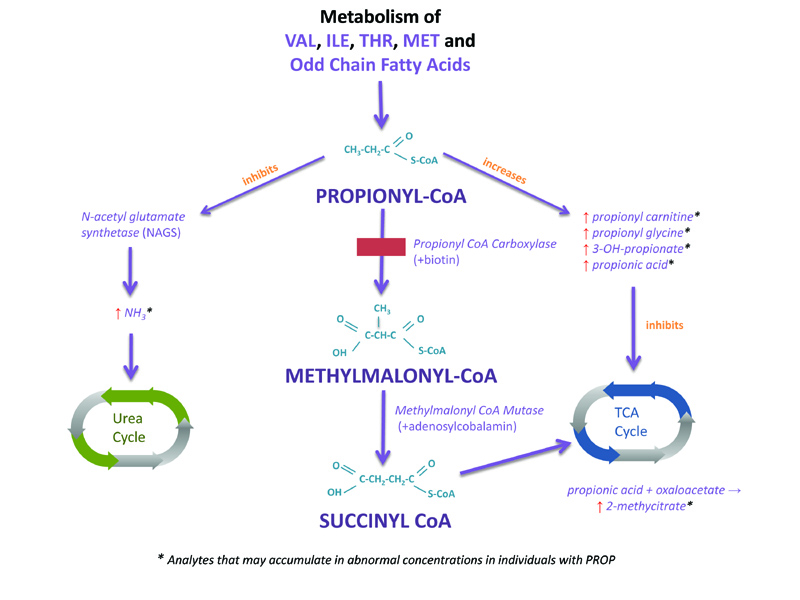
Propionyl CoA is an intermediate in the catabolism of the amino acids leucine (LEU), isoleucine (ILE), threonine (THR) and methionine (MET), and of odd chain fatty acids. When the pathway is blocked by the loss of catalytic activity of the enzyme propionyl CoA carboxylase, there is an accumulation of propionyl CoA. The propionyl CoA enters minor pathways to be converted to propionylcarnitine, propionyl glycine, 3-OH propionic acid and propionic acid. Propionic acid can disrupt the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) by combining with oxaloacetate to form 2-methylcitrate.There is also inhibition of N-acetyl glutamate synthetase (NAGS) disrupting the urea cycle and causing hyperammonemia.
View a full size PDF of this image
The goals of medical nutrition therapy in PROP are to:
- Reduce toxic metabolite accumulation by restricting dietary sources of VAL, ILE, MET and THR while maintaining normal concentrations of plasma amino acids
- Avoid prolonged fasting to reduce production of odd chain fatty acids
- Reduce catabolism
- Promote anabolism
- Promote normal growth, development and health maintenance


